Depression
Adult: 25 mg once daily at bedtime, may be increased to 50 mg after 2 wk, if necessary.
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Depression Adult: 25 mg once daily at bedtime, may be increased to 50 mg after 2 wk, if necessary.
|
|
Hepatic Impairment
Contraindicated.
|
|
Administration
May be taken with or without food.
|
|
Contraindications
Dementia. Elderly >75 yr. Hepatic impairment (i.e. active liver disease, cirrhosis) or serum transaminases >3 times upper limit of normal (ULN). Concomitant use w/ potent CYP1A2 inhibitors.
|
|
Special Precautions
Patient w/ bipolar disorder, mania, hypomania, DM, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, pre-treatment elevated transaminases, history of suicide-related events or those who exhibit significant degree of suicidal ideation. Obese and alcoholic patients, smokers. Moderate to severe renal impairment.
|
|
Adverse Reactions
Significant: Suicidal thoughts and behaviour, increased liver enzymes, hepatitis, jaundice.
Nervous: Headache, migraine, insomnia, anxiety, delirium, tremor, aggression, agitation, nightmares, hallucinations, paraesthesia, restless leg syndrome, fatigue. GI: Nausea, abdominal pain, dry mouth, dyspepsia, diarrhoea, constipation, vomiting. Resp: Nasopharyngitis. Musculoskeletal: Back pain. Ophthalmologic: Blurred vision. Dermatologic: Rash, pruritus, urticaria, eczema, hyperhidrosis. Immunologic: Influenza. Potentially Fatal: Hepatic failure. |
|
Patient Counseling Information
This drug may cause dizziness or somnolence, if affected, do not drive or operate machinery.
|
|
Monitoring Parameters
Perform LFT at baseline, before dose increase, at 3, 6, 12, 24 wk of treatment, then as clinically indicated. Monitor for signs/symptoms of hepatic injury (e.g. dark urine, light coloured stools, yellow skin/eyes, unexplained fatigue, pain in the upper right abdomen).
|
|
Overdosage
Symptoms: Epigastralgia, fatigue, agitation, somnolence, dizziness, anxiety, tension, malaise. Management: Symptomatic treatment.
|
|
Drug Interactions
Increased exposure w/ moderate CYP1A2 inhibitors (estrogen, enoxacin, propranolol). Decreased bioavailability w/ rifampicin.
Potentially Fatal: Potent CYP1A2 inhibitors (e.g. fluvoxamine, ciprofloxacin) may markedly increase agomelatine exposure. |
|
Food Interaction
Avoid alcohol.
|
|
Action
Description:
Mechanism of Action: Agomelatine, a melatonin receptor (MT1 and MT2) agonist and serotonin (5-HT2C) antagonist, increases norepinephrine and dopamine release in the prefrontal cortex and has no influence on the extracellular levels of serotonin. It induces a phase advance of sleep, body temp decline, and melatonin onset. It has no effect on monoamine uptake and no affinity for α or β adrenergic, cholinergic, dopaminergic, histaminergic, and benzodiazepine receptors. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Rapidly and well absorbed. Absolute bioavailability: <5%. Time to peak plasma concentration: W/in 1-2 hr. Distribution: Plasma protein binding: Approx 95%. Metabolism: Rapidly metabolised in the liver, mainly by CYP1A2 enzyme, and to a lesser extent by CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 enzymes. Excretion: Mainly via urine (80%, as inactive metabolites). Plasma half-life: 1-2 hr. |
|
Chemical Structure
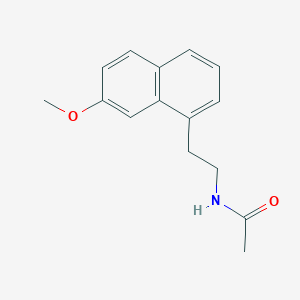 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. Agomelatine, CID=82148, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Agomelatine (accessed on Jan. 20, 2020) |
|
Storage
Store below 30°C.
|
|
MIMS Class
|
|
ATC Classification
N06AX22 - agomelatine ; Belongs to the class of other antidepressants.
|
|
References
Buckingham R (ed). Agomelatine. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 04/04/2017. Joint Formulary Committee. Agomelatine. British National Formulary [online]. London. BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 04/04/2017.
|