Pulmonary arterial hypertension
Adult: In patients w/ WHO functional class II and III PAH (idiopathic, heritable, or associated w/ connective tissue diseases): Initially, 5 mg once daily, may be increased up to 10 mg once daily if necessary.
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Pulmonary arterial hypertension Adult: In patients w/ WHO functional class II and III PAH (idiopathic, heritable, or associated w/ connective tissue diseases): Initially, 5 mg once daily, may be increased up to 10 mg once daily if necessary.
|
|
Special Patient Group
Patients taking ciclosporin: Max: 5 mg once daily.
|
|
Hepatic Impairment
Severe: Contraindicated.
|
|
Administration
May be taken with or without food. Swallow whole, do not split/chew/crush.
|
|
Contraindications
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Severe hepatic impairment or clinically significant elevated hepatic aminotransferases (>3 times the upper limit of normal). Pregnancy and lactation.
|
|
Special Precautions
Patient w/ pulmonary veno-occlusive disease, significant anaemia. Severe renal (CrCl <30 ml/min) and moderate hepatic impairment. Patients taking concomitant ciclosporin.
|
|
Adverse Reactions
Significant: Autoimmune hepatitis (e.g. exacerbation of underlying autoimmune hepatitis, hepatic injury, hepatic enzyme elevations), reduced Hb and haematocrit, fluid retention, peripheral oedema, acute pulmonary oedema, decreased sperm count.
Nervous: Headache, dizziness, fatigue, asthenia. CV: Palpitation, cardiac failure, flushing, hypotension, syncope, chest pain. GI: Diarrhoea, vomiting, nausea, abdominal pain, constipation. Resp: Dyspnoea, nasopharyngitis, nasal congestion, epistaxis, sinusitis, rhinitis. |
|
Patient Counseling Information
This drug may cause dizziness, asthenia, hypotension, or fatigue, if affected, do not drive or operate machinery.
|
|
Monitoring Parameters
Monitor for signs of hepatic injury, significant peripheral oedema. Monitor ALT and AST, Hb and haematocrit levels. Obtain mthly pregnancy test during treatment.
|
|
Overdosage
Symptoms: Headache, dizziness, flushing, nausea, nasal congestion, and potential hypotension. Management: In case of hypotension, give active CV support.
|
|
Drug Interactions
Increased exposure w/ ciclosporin. Rifampicin may cause transient increase in ambrisentan exposure.
|
|
Action
Description:
Mechanism of Action: Ambrisentan, an endothelin antagonist, is selective on endothelin type A (ETA) receptor. Endothelin is a potent vasoconstrictor which plays a pathogenic role in pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Blockade of endothelin receptor leads to vasodilation and inhibition of smooth muscle proliferation. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Absorbed rapidly from the GI tract. Time to peak plasma concentration: Approx 2 hr. Distribution: Plasma protein binding: 99%, mainly to albumin and to a lesser extent to α1-acid glycoprotein. Metabolism: Metabolised via glucuronidation by several uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) isoenzymes to ambrisentan glucuronide and via oxidation, mainly by CYP3A4 and to a lesser extent by CYP3A5 and CYP2C19, to form 4-hydroxymethyl ambrisentan. Excretion: Mainly via bile; urine (22%, 3.3% as unchanged drug). Terminal elimination half-life: Approx 15 hr. |
|
Chemical Structure
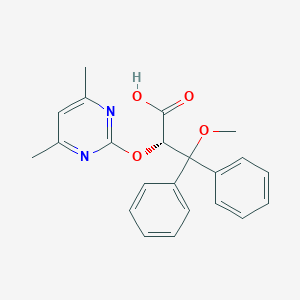 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. Ambrisentan, CID=6918493, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Letairis (accessed on Jan. 20, 2020) |
|
Storage
Store between 15-30°C.
Wear gloves during receiving, unpacking, and placing in storage. |
|
MIMS Class
|
|
ATC Classification
C02KX02 - ambrisentan ; Belongs to the class of other antihypertensives. Used in the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension.
|
|
References
Anon. Ambrisentan. Lexicomp Online. Hudson, Ohio. Wolters Kluwer Clinical Drug Information, Inc. https://online.lexi.com. Accessed 31/07/2017. Buckingham R (ed). Ambrisentan. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 31/07/2017. Joint Formulary Committee. Ambrisentan. British National Formulary [online]. London. BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 31/07/2017. Letairis Tablets (Gilead Sciences, Inc.). DailyMed. Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/. Accessed 31/07/2017. McEvoy GK, Snow EK, Miller J et al (eds). Ambrisentan. AHFS Drug Information (AHFS DI) [online]. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 31/07/2017.
|