Oedema
Adult: Initially, 5-10 mg daily. Start w/ 2.5 mg once daily if used w/ other diuretics or antihypertensives. Max: 20 mg daily.
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Oedema Adult: Initially, 5-10 mg daily. Start w/ 2.5 mg once daily if used w/ other diuretics or antihypertensives. Max: 20 mg daily.
|
|
Renal Impairment
Severe: Avoid use.
|
|
Administration
Should be taken with food.
|
|
Contraindications
Hyperkalaemia, Addison's disease, anuria, acute or chronic renal insufficiency, diabetic nephropathy.
|
|
Special Precautions
Patient w/ DM, at risk of metabolic or resp acidosis. Renal and hepatic impairment. Elderly. Pregnancy and lactation.
|
|
Adverse Reactions
Abdominal pain, GI bleeding, thirst, dry mouth, diarrhoea, constipation, anorexia, jaundice, flatulence, dyspepsia, vomiting, nausea, angina, arrhythmias, palpitation, postural hypotension, dyspnoea, cough, nasal congestion, confusion, headache, insomnia, weakness, tremor, agitation, dizziness, malaise, paraesthesia, encephalopathy, urinary disturbances, sexual dysfunction, hyperkalaemia, muscle cramps, arthralgia, raised intraocular pressure, visual disturbance, tinnitus, alopecia, pruritus, rash.
|
|
Monitoring Parameters
Monitor serum electrolytes, BP and renal function.
|
|
Drug Interactions
Increased risk of hyperkalaemia w/ other K-sparing diuretics, K supplements, angiotensin II receptor antagonists, ACE inhibitors, trilostane. Increased risk of nephrotoxicity w/ ciclosporin and NSAIDs. Severe hyponatraemia may occur w/ thiazide or chlorpropamide. May reduce ulcer-healing properties w/ carbenoxolone. May enhance the effect of other antihypertensives.
|
|
Food Interaction
Food reduces bioavailability.
|
|
Lab Interference
May falsely increase serum digoxin levels done by radioimmunoassay.
|
|
Action
Description:
Mechanism of Action: Amiloride is a weak diuretic which acts mainly on the distal renal tubules. It increases the excretion of Na and reduces the excretion of K. It diminishes kaliuretic effects of other diuretics, and may produce an additional natriuretic effect. Onset: 2 hr. Duration: 24 hr. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Incompletely absorbed from the GI tract. Bioavailability is reduced by food. Bioavailability: Approx 50%. Time to peak plasma concentration: Approx 3-4 hr. Distribution: Widely distributed in the tissues. Volume of distribution: 350-380 L. Plasma protein binding: 23%. Metabolism: Not metabolised. Excretion: Via urine (as unchanged drug). Plasma half-life: 6-9 hr; terminal half-life: ≥20 hr. |
|
Chemical Structure
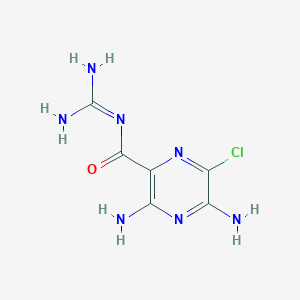 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. Amiloride, CID=16231, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Amiloride (accessed on Jan. 20, 2020) |
|
Storage
Store between 15-30°C.
|
|
MIMS Class
|
|
References
Amiloride Hydrochloride Anhydrous Tablet (Par Pharmaceutical Inc.). DailyMed. Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/. Accessed 11/11/2014. Anon. Amiloride. Lexicomp Online. Hudson, Ohio. Wolters Kluwer Clinical Drug Information, Inc. https://online.lexi.com. Accessed 11/11/2014. Buckingham R (ed). Amiloride Hydrochloride. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 11/11/2014. Joint Formulary Committee. Amiloride Hydrochloride. British National Formulary [online]. London. BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 11/11/2014. McEvoy GK, Snow EK, Miller J et al (eds). Amiloride Hydrochloride. AHFS Drug Information (AHFS DI) [online]. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 11/11/2014.
|