Hypertension
Adult: Each tab contains amlodipine (mg)/valsartan (mg): 5/80, 5/160, 5/320, 10/160, or 10/320: Individualised dosing according to patient condition. Recommended dose: 1 tab once daily, may be titrated as needed.
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Hypertension Adult: Each tab contains amlodipine (mg)/valsartan (mg): 5/80, 5/160, 5/320, 10/160, or 10/320: Individualised dosing according to patient condition. Recommended dose: 1 tab once daily, may be titrated as needed.
|
|
Hepatic Impairment
Mild to moderate: Valsartan: 80 mg. Severe: Contraindicated.
|
|
Administration
May be taken with or without food.
|
|
Contraindications
Biliary cirrhosis or cholestasis, severe hypotension, shock (i.e. cardiogenic shock). Severe hepatic impairment. Pregnancy. Concomitant use w/ ACE inhibitors or aliskiren-containing product in patients w/ DM or renal impairment (CrCl <60 mL/min).
|
|
Special Precautions
Patient w/ Na- or volume-depletion, idiopathic or hereditary angioedema, biliary obstructive disorders, primary hyperaldosteronism, severe obstructive coronary artery disease, severe CHF, recent MI, mitral or aortic stenosis, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy w/ outflow tract obstruction, DM. Patient undergoing surgery or dialysis. Renal (e.g. chronic kidney disease, unilater/bilateral renal artery stenosis) and mild to moderate hepatic impairment. Lactation.
|
|
Adverse Reactions
Significant: Hypotension, angina, acute renal failure, hyperkalaemia, peripheral oedema. Rarely, angioedema.
Nervous: Headache, anxiety, somnolence, syncope, vertigo, fatigue, asthenia, dizziness, paraesthesia. CV: Orthostatic hypotension, tachycardia, palpitations. GI: Nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhoea, anorexia, constipation, dry mouth. Resp: Nasopharyngitis, upper resp tract infection, cough. Genitourinary: Increased BUN. Dermatologic: Pitting and facial oedema, rash, erythema, Immunologic: Influenza. |
|
Patient Counseling Information
This drug may cause dizziness, headache, fatigue, or nausea, if affected, do not drive or operate machinery.
|
|
Monitoring Parameters
Monitor electrolyte panels at baseline and periodically, urinalysis, BP, heart rate, and renal and liver functions. Monitor serum K periodically and during dose titration esp in patients w/ heart failure.
|
|
Drug Interactions
Increased risk of hypotension w/ TCAs, diuretics, α-blockers. Increased exposure of amlodipine w/ moderate or strong CYP3A4 enzyme inhibitors (e.g. protease inhibitors, azole antifungals, erythromycin, clarithromycin, verapamil, diltiazem). Decreased plasma concentration of amlodipine w/ CYP3A4 enzyme inducers (e.g. rifampicin). Valsartan may cause a reversible increase in serum lithium concentration and toxicity. Concomitant use of valsartan w/ NSAIDs may cause an attenuation of antihypertensive effects, worsen renal function, and increase serum K. Increased risk of hyperkalaemia w/ K-sparing diuretics, K supplements or K-containing salt substitutes w/ valsartan. Concomitant admin of organic anion transporter protein (OATP) 1B1 (e.g. ciclosporin, rifampicin) or multidrug resistance protein (MRP2) (e.g. ritonavir) inhibitors may increase systemic exposure of valsartan.
Potentially Fatal: Dual blockade of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) by concomitant use w/ ACE inhibitors or aliskiren may cause an increased risk of hypotension, hyperkaelemia, and acute renal failure. |
|
Food Interaction
Increased BP-lowering effects of amlodipine w/ grapefruit or grapefruit juice. Decreased plasma concentration of amlodipine w/ St. John’s wort. Food may decrease rate and extent of absorption.
|
|
Action
Description:
Mechanism of Action: Amlodipine, a dihydropyridine Ca channel blocker, reduces peripheral vascular resistance and BP by producing peripheral arterial vasodilation through inhibition of Ca ion transmembrane influx into cardiac and vascular smooth muscles. Valsartan, a nonpetide tetrazole derivative, is an angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptor antagonist producing its BP lowering effects by selectively blocking the binding of angiotensin II to angiotensin type 1 (AT1) receptors on numerous tissues including vascular smooth muscles and the adrenal gland, thereby resulting in antagonism of AT1-induced vasoconstriction, aldosterone synthesis and release, cardiac stimulation, and Na renal reabsorption. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Amlodipine: Well absorbed. Bioavailability: 64-80%. Time to peak plasma concentration: 6-12 hr. Valsartan: Rapidly absorbed. Food may decrease rate and extent of absorption. Bioavailability: 23%. Time to peak plasma concentration: 2-4 hr. Distribution: Amlodipine: Volume of distribution: Approx 21 L/kg. Plasma protein binding: Approx 97.5%. Valsartan: Plasma protein binding: 94-97%, mainly to albumin. Metabolism: Amlodipine: Extensively metabolised in the liver to inactive metabolites. Valsartan: Minimal metabolism by CYP2C9 enzyme. Excretion: Amlodipine: Via urine (60% as metabolites, 10% as unchanged drug). Terminal elimination half-life: 30-50 hr. Valsartan: Via faeces (83%) and urine (13%). Terminal elimination half-life: 6 hr. |
|
Chemical Structure
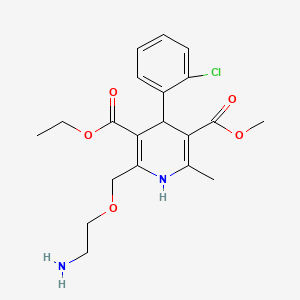 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 2162, Amlodipine. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Amlodipine. Accessed Oct. 26, 2023. 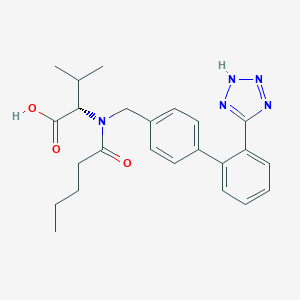 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 60846, Valsartan. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Valsartan. Accessed Oct. 25, 2023. |
|
Storage
Store below 30°C. Protect from moisture.
|
|
MIMS Class
|
|
ATC Classification
C09DB01 - valsartan and amlodipine ; Belongs to the class of angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) and calcium channel blockers. Used in the treatment of cardiovascular disease.
|
|
References
Anon. Amlodipine and Valsartan. Lexicomp Online. Hudson, Ohio. Wolters Kluwer Clinical Drug Information, Inc. https://online.lexi.com. Accessed 13/06/2017. Anon. Valsartan. AHFS Clinical Drug Information [online]. Bethesda, MD. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. https://www.ahfscdi.com. Accessed 13/06/2017. Buckingham R (ed). Amlodipine. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 13/06/2017. Buckingham R (ed). Valsartan. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 13/06/2017. Exforge Tablet, Film Coated (Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation). DailyMed. Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/. Accessed 13/06/2017. Joint Formulary Committee. Amlodipine with Valsartan. British National Formulary [online]. London. BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 13/06/2017. McEvoy GK, Snow EK, Miller J et al (eds). Amlodipine Besylate. AHFS Drug Information (AHFS DI) [online]. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 13/06/2017.
|