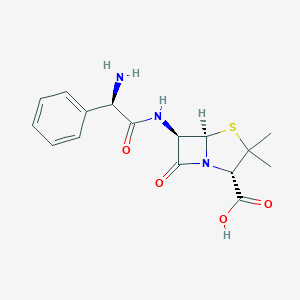
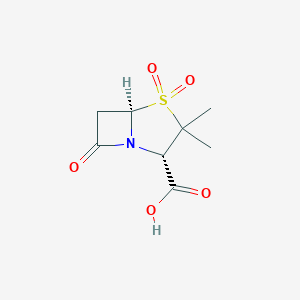
Bacterial septicaemia, Bone and joint infections, Gynaecological infections, Intra-abdominal infections, Lower respiratory tract infections, Pyelonephritis, Skin and skin structure infections, Upper respiratory tract infections, Urinary tract infection
Adult: Available preparations:
Ampicillin 250 mg and sulbactam 125 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Ampicillin 500 mg and sulbactam 250 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Ampicillin 1,000 mg and sulbactam 500 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Ampicillin 2,000 mg and sulbactam 1,000 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Recommended dose is expressed as a total of ampicillin/sulbactam combination. Dosage is individualised based on the type or severity of the infection and renal function of the patient. Usual dose range: 1,500-12,000 mg daily in divided doses 6 or 8 hourly via IV inj or IV infusion over 15-30 minutes, or via deep IM inj. Max: 4,000 mg sulbactam daily. In less severe cases, doses may be given 12 hourly. Treatment duration: 5-14 days, may be extended (or additional ampicillin may be given) in severely ill cases.
Child: Available preparations:
Ampicillin 250 mg and sulbactam 125 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Ampicillin 500 mg and sulbactam 250 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Ampicillin 1,000 mg and sulbactam 500 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Ampicillin 2,000 mg and sulbactam 1,000 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Neonates, infants, children 150 mg/kg daily (corresponding to 100 mg ampicillin/kg/day and 50 mg sulbactam/kg/day) in divided doses 6 or 8 hourly via IV inj or IV infusion over 15-30 minutes, or via deep IM inj. Neonates During the 1st week of life (particularly preterms): 75 mg/kg daily (corresponding to 50 mg ampicillin/kg/day and 25 mg sulbactam/kg/day) in divided doses 12 hourly. Alternatively, for skin infections: ≥1 year 300 mg/kg daily (corresponding to 200 mg ampicillin/kg/day and 100 mg sulbactam/kg/day) via IV infusion in divided doses 6 hourly for up to 14 days; ≥40 kg: Same as adult dose. Dosage recommendations may vary among countries and individual products (refer to detailed product guideline).
Ampicillin 250 mg and sulbactam 125 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Ampicillin 500 mg and sulbactam 250 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Ampicillin 1,000 mg and sulbactam 500 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Ampicillin 2,000 mg and sulbactam 1,000 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Recommended dose is expressed as a total of ampicillin/sulbactam combination. Dosage is individualised based on the type or severity of the infection and renal function of the patient. Usual dose range: 1,500-12,000 mg daily in divided doses 6 or 8 hourly via IV inj or IV infusion over 15-30 minutes, or via deep IM inj. Max: 4,000 mg sulbactam daily. In less severe cases, doses may be given 12 hourly. Treatment duration: 5-14 days, may be extended (or additional ampicillin may be given) in severely ill cases.
Child: Available preparations:
Ampicillin 250 mg and sulbactam 125 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Ampicillin 500 mg and sulbactam 250 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Ampicillin 1,000 mg and sulbactam 500 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Ampicillin 2,000 mg and sulbactam 1,000 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Neonates, infants, children 150 mg/kg daily (corresponding to 100 mg ampicillin/kg/day and 50 mg sulbactam/kg/day) in divided doses 6 or 8 hourly via IV inj or IV infusion over 15-30 minutes, or via deep IM inj. Neonates During the 1st week of life (particularly preterms): 75 mg/kg daily (corresponding to 50 mg ampicillin/kg/day and 25 mg sulbactam/kg/day) in divided doses 12 hourly. Alternatively, for skin infections: ≥1 year 300 mg/kg daily (corresponding to 200 mg ampicillin/kg/day and 100 mg sulbactam/kg/day) via IV infusion in divided doses 6 hourly for up to 14 days; ≥40 kg: Same as adult dose. Dosage recommendations may vary among countries and individual products (refer to detailed product guideline).
Intramuscular, Intravenous
Prophylaxis of surgical infections
Adult: Available preparations:
Ampicillin 250 mg and sulbactam 125 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Ampicillin 500 mg and sulbactam 250 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Ampicillin 1,000 mg and sulbactam 500 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Ampicillin 2,000 mg and sulbactam 1,000 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Recommended dose is expressed as a total of ampicillin/sulbactam combination. In patients undergoing pelvic or abdominal surgery in which peritoneal contamination may be present, or in termination of pregnancy or caesarean section: 1,500-3,000 mg via IV or IM at induction of anaesthesia, may be repeated 6-8 hourly. Administration may be discontinued 24 hours after the majority of surgical procedures, unless therapeutic use is clinically indicated.
Ampicillin 250 mg and sulbactam 125 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Ampicillin 500 mg and sulbactam 250 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Ampicillin 1,000 mg and sulbactam 500 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Ampicillin 2,000 mg and sulbactam 1,000 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Recommended dose is expressed as a total of ampicillin/sulbactam combination. In patients undergoing pelvic or abdominal surgery in which peritoneal contamination may be present, or in termination of pregnancy or caesarean section: 1,500-3,000 mg via IV or IM at induction of anaesthesia, may be repeated 6-8 hourly. Administration may be discontinued 24 hours after the majority of surgical procedures, unless therapeutic use is clinically indicated.
Intramuscular, Intravenous
Uncomplicated gonorrhoea
Adult: Available preparations:
Ampicillin 250 mg and sulbactam 125 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Ampicillin 500 mg and sulbactam 250 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Ampicillin 1,000 mg and sulbactam 500 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Ampicillin 2,000 mg and sulbactam 1,000 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Recommended dose is expressed as a total of ampicillin/sulbactam combination. In combination with oral probenecid: 1,500 mg as single dose via IV or IM.
Ampicillin 250 mg and sulbactam 125 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Ampicillin 500 mg and sulbactam 250 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Ampicillin 1,000 mg and sulbactam 500 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Ampicillin 2,000 mg and sulbactam 1,000 mg powder for solution for inj or infusion
Recommended dose is expressed as a total of ampicillin/sulbactam combination. In combination with oral probenecid: 1,500 mg as single dose via IV or IM.




 Sign Out
Sign Out