Active progressive rheumatoid arthritis
Adult: Initially, 3 mg bid, or if tolerated, 6 mg once daily. If response is inadequate after 6 mth, increase dose to 3 mg tid. If response is still inadequate 3 mth later, discontinue treatment.
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Active progressive rheumatoid arthritis Adult: Initially, 3 mg bid, or if tolerated, 6 mg once daily. If response is inadequate after 6 mth, increase dose to 3 mg tid. If response is still inadequate 3 mth later, discontinue treatment.
|
|
Administration
Should be taken with food. Take after meals or a light snack.
|
|
Contraindications
History of toxicity to gold compounds including necrotizing enterocolitis, pulmonary fibrosis, severe chronic dermatitis (e.g. exfoliative dermatitis, severe urticaria/eczema), severe haematological disorder (e.g. bone marrow aplasia, thrombocytopenia, leucopenia, aplastic anaemia). Concomitant use w/ clozapine, antimalarial agents, penicillamine, and immunosuppressive agents. Lactation.
|
|
Special Precautions
Patient w/ inflammatory bowel disease, history of bone marrow depression, acute porphyria, DM, HTN, CHF. Patient undergoing radiotherapy. Hepatic (e.g. hepatocellular disease) and renal impairment (e.g. progressive renal failure). Pregnancy.
|
|
Adverse Reactions
Nausea w/ or w/o vomiting, abdominal pain, loose stools/diarrhoea, anorexia, flatulence, dyspepsia, dysgeusia, constipation; rash, pruritus, hair loss, urticaria, photosensitivity; stomatitis, conjunctivitis, glossitis; anaemia, leucopenia, granulocytopenia, thrombocytopenia, eosinophilia; haematuria, proteinuria, increased BUN and serum creatinine; elevated liver enzymes.
|
|
Monitoring Parameters
Monitor CBC w/ differential, platelet count, and urinalysis at baseline and during therapy. Monitor hepatic and renal function.
|
|
Overdosage
Symptoms: Dizziness, headache, flushing, tachyarrhythmia, palpitation, thrombocytopenia, kidney and liver effects. Management: Supportive treatment. Induce emesis or employ gastric lavage.
|
|
Drug Interactions
Altered absorption and increased toxicity w/ drugs affecting GI motility (e.g. prokinetics, loperamide, senna). May cause blood dyscrasias w/ phenylbutazone, oxyphenbutazone, levamisole, high-dose corticosteroids. May increase risk of vasomotor reaction w/ ACE inhibitors. May cause renal impairment or proteinuria w/ aminoglycosides, amphotericin B, penicillins, phenytoin, sulfonamides, NSAIDs, aciclovir. May increase plasma concentration of phenytoin.
Potentially Fatal: May cause an additive risk of haematological toxicity and renal AR w/ clozapine, antimalarial agents (e.g. chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, atovaquone/proguanil, mefloquine, quinine), penicillamine. May cause serious hepatotoxicity and haematological toxicity w/ immunosuppressive agents (e.g. leflunomide). |
|
Lab Interference
May enhance response to tuberculin skin test.
|
|
Action
Description:
Mechanism of Action: Auranofin is a synthetic gold compound that exhibits anti-inflammatory, antiarthritic, and immunomodulating effects. It is taken up by macrophages, resulting in inhibition of phagocytosis and lysosomal membrane stabilisation. Additionally, it inhibits prostaglandin synthesis and decreases serum rheumatoid factor, complement activation, and lysosomal enzyme release. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Incompletely (approx 25%) absorbed from the GI tract. Distribution: Penetrates into synovial fluid; approx 40% is associated w/ RBCs. Plasma protein binding: 60%. Metabolism: Rapidly metabolised. Excretion: Mainly via faeces (84-92%); urine (9-17%, approx 60% as absorbed gold. Elimination half-life: 21-31 days. |
|
Chemical Structure
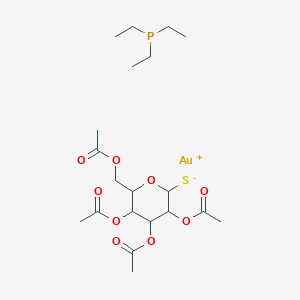 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. CID=24199313, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/24199313 (accessed on Jan. 21, 2020) |
|
Storage
Store between 15-30°C. Protect from light.
|
|
ATC Classification
M01CB03 - auranofin ; Belongs to the class of gold preparations of antirheumatic agents.
|
|
References
Anon. Auranofin. Lexicomp Online. Hudson, Ohio. Wolters Kluwer Clinical Drug Information, Inc. https://online.lexi.com. Accessed 17/10/2016. Buckingham R (ed). Auranofin. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 17/10/2016. McEvoy GK, Snow EK, Miller J et al (eds). Auranofin. AHFS Drug Information (AHFS DI) [online]. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 17/10/2016. Ridaura Capsule (Prometheus Laboratories Inc.). DailyMed. Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/. Accessed 17/10/2016.
|