Hyperlipidaemias
Adult: As conventional tab: 200 mg tid, may increase dose gradually, to avoid GI symptoms, over 5-7 days. Maintenance: 200 mg bid. As modified-release tab: 400 mg once daily.
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Hyperlipidaemias Adult: As conventional tab: 200 mg tid, may increase dose gradually, to avoid GI symptoms, over 5-7 days. Maintenance: 200 mg bid. As modified-release tab: 400 mg once daily.
|
||||||||||
|
Renal Impairment
Dialysis patients: Contraindicated.
|
||||||||||
|
Hepatic Impairment
Severe:
Contraindicated.
|
||||||||||
|
Administration
Should be taken with food.
|
||||||||||
|
Contraindications
Gallbladder disorder, hypoalbuminaemia (e.g. nephrotic syndrome). Severe hepatic or renal impairment [CrCl <15 mL/min (conventional tab); CrCl <60 mL/min (modified-release tab)], patients undergoing dialysis. Pregnancy and lactation. Concomitant use of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (in patients w/ risk factors for myopathy), perhexiline maleate and MAOIs.
|
||||||||||
|
Special Precautions
Renal impairment [(CrCl ≥15 mL/min (conventional tab)].
|
||||||||||
|
Adverse Reactions
Anorexia, nausea, GI upset, headache, dizziness, vertigo, fatigue, skin rashes, pruritus, urticaria, photosensitivity, alopecia, impotence, anaemia, leucopoenia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, decreased appetite, peripheral neuropathy, paraesthesia, depression, insomnia, abdominal pain, constipation, dyspepsia, diarrhoea, abdominal distension, pancreatitis, cholestasis, cholelithiasis, Stevens-Johnsons syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, myalgia, myopathy, myositis, erectile dysfunction, interstitial lung disease, acute renal failure. Rarely, rhabdomyolysis.
|
||||||||||
|
Patient Counseling Information
This drug may cause dizziness, if affected, do not drive or operate machinery.
|
||||||||||
|
Monitoring Parameters
Perform serum lipids, cholesterol and triglyceride tests, fasting glucose, creatinine, and CBC periodically, and LFT after 3-6 mth.
|
||||||||||
|
Overdosage
Symptoms: Rhabdomyolysis. Management: Symptomatic treatment.
|
||||||||||
|
Drug Interactions
Anion-exchange resins (e.g. cholestyramine) inhibit bezafibrate absorption, take at least 2 hr apart. May increase serum concentration of anticoagulants. Increased risk of renal impairment when used w/ immunosuppressants. May potentiate the therapeutic effect of sulfonylureas and insulin. Estrogens may increase lipid levels, dosing should be individualised in patients taking oestrogen-containing contraceptives.
Potentially Fatal: Potential hepatotoxic effect when used w/ perhexiline maleate or MAOIs. Increased risk of myopathy in predisposed patients who are taking HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. |
||||||||||
|
Action
Description:
Mechanism of Action: Bezafibrate, a fibric acid derivative, reduces VLDL and LDL while increasing HDL levels. It increases the activity of triglyceride lipases involved in the catabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and inhibits hepatic acetyl co-enzyme A carboxylase synthesis. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Rapid and almost completely absorbed in the GI tract. Time to peak serum concentration: 1-2 hr (conventional); 3-4 hr (modified-release). Distribution: Volume of distribution: Approx 17 L. Plasma protein binding: 94-96%. Excretion: Via urine (95%, 50% as unchanged drug and 20% as glucuronides); faeces (3%). Elimination half-life: 1-2 hr. |
||||||||||
|
Chemical Structure
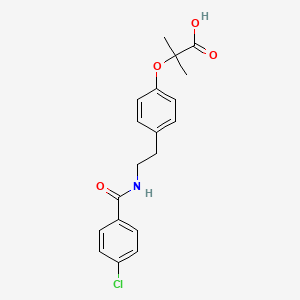 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. Bezafibrate, CID=39042, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Bezafibrate (accessed on Jan. 21, 2020) |
||||||||||
|
Storage
Store between 15-30°C.
|
||||||||||
|
MIMS Class
|
||||||||||
|
ATC Classification
C10AB02 - bezafibrate ; Belongs to the class of fibrates. Used in the treatment of hyperlipidemia.
|
||||||||||
|
References
Actavis New Zealand Limited. Bezalip and Bezalip Retard Tablets data sheet 1 July 2013. Medsafe. http://www.medsafe.govt.nz/. Accessed 09/08/2016 . Anon. Bezafibrate. Lexicomp Online. Hudson, Ohio. Wolters Kluwer Clinical Drug Information, Inc. https://online.lexi.com. Accessed 09/08/2016 . Buckingham R (ed). Bezafibrate. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 09/08/2016 . Joint Formulary Committee. Bezafibrate. British National Formulary [online]. London. BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 09/08/2016 .
|