Insomnia
Adult: For short-term treatment: 250 mcg at bedtime for up to 2 wk.
Elderly: 125 mcg at bedtime.
Elderly: 125 mcg at bedtime.
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Insomnia Adult: For short-term treatment: 250 mcg at bedtime for up to 2 wk.
Elderly: 125 mcg at bedtime. |
|
Special Patient Group
Debiliated patients: 125 mcg at bedtime.
|
|
Contraindications
Acute pulmonary insufficiency, sleep apnoea syndrome, myasthenia gravis, psychoses, acute narrow-angle glaucoma. Severe hepatic impairment. Pregnancy and lactation.
|
|
Special Precautions
Patient in whom a drop in BP might lead to cardiac complications; chronic pulmonary insufficiency. Prolonged use may cause dependence. Avoid abrupt withdrawal. Renal and mild to moderate hepatic impairment.
|
|
Adverse Reactions
Paradoxical reactions (e.g. acute hyperexcitability, anxiety, hallucinations, increased muscle spasticity, rage, insomnia, sleep disturbances and stimulation); drowsiness, fatigue, ataxia; sedation and sleepiness, depression, lethargy, apathy, hypoactivity, lightheadedness, disorientation, restlessness, confusion, delirium, headache, slurred speech, dysarthria, syncope, vertigo, tinnitus, dizziness, nervousness, vivid dreams, psychomotor retardation; constipation, diarrhoea, dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, increased salivation; incontinence, dysuria, enuresis, changes in libido, urinary retention, menstrual irregularities; bradycardia, tachycardia, HTN, hypotension, palpitations; visual disturbances, diplopia; urticaria, pruritus, skin rash, dermatitis; hepatic dysfunction (e.g. hepatitis, jaundice), blood dyscrasias (e.g. agranulocytosis, anaemia, thrombocytopenia, eosinophilia).
|
|
Patient Counseling Information
May impair ability to drive or operate machinery.
|
|
Overdosage
Symptoms: Somnolence, confusion, coma, reduced or absent reflexes, resp depression, hypotension. Management: Induce vomiting if the patient is conscious; employ gastric lavage if unconscious. Supportive measures along w/ IV fluids should be employed. Maintain an adequate airway. May administer norepinephrine or metaraminol to treat hypotension or barbiturates if excitation occurs. Flumazenil may be useful as an antidote.
|
|
Drug Interactions
May potentiate the effect of centrally-acting drugs (e.g. neuroleptics, tranquilisers, antidepressants, hypnotics, antiepileptics, antihistamines, analgesics and anaesth). May increase the effect of muscle relaxants. Increased effect w/ CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g. itraconazole, ketoconazole). Decreased effect w/ CYP3A4 inducers (e.g. carbamazepine, efavirenz).
|
|
Food Interaction
Increased CNS effect w/ alcohol. Decreased effect w/ St John's wort.
|
|
Action
Description:
Mechanism of Action: Brotizolam act as positive allosteric modulator on the γ-amino butyric acid (GABA)-A receptor. It binds to the pocket created by the α and γ subunits. This alteration, in turn, induces a conformational change in the GABA-A receptor's Cl channel that hyperpolarises the cell and accounts for GABA's inhibitory effect throughout the CNS. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Absorbed from the GI tract. Bioavailability: Approx 70%. Time to peak plasma concentration: 0.5-3 hr. Distribution: Plasma protein binding: Approx 90%, to albumin. Excretion: Via urine (approx 65%) and faeces (approx 22%). Half-life: 3.1-8.4 hr. |
|
Chemical Structure
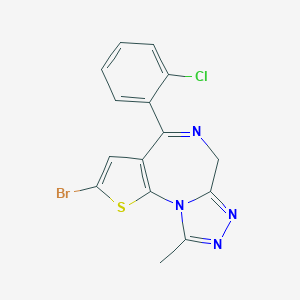 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. Brotizolam, CID=2451, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Brotizolam (accessed on Jan. 22, 2020) |
|
MIMS Class
|
|
ATC Classification
N05CD09 - brotizolam ; Belongs to the class of benzodiazepine derivatives. Used as hypnotics and sedatives.
|
|
References
Griffin CE III, Kaye AM, Bueno FR et al. Benzodiazepine Pharmacology and Central Nervous
System–Mediated Effects. The Ochsner Journal. 2013;13(2):214–223. Accessed 03/12/2014. PMID: 23789008 Anon. Brotizolam. Lexicomp Online. Hudson, Ohio. Wolters Kluwer Clinical Drug Information, Inc. https://online.lexi.com. Accessed 03/12/2014. Buckingham R (ed). Brotizolam. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 03/12/2014.
|