Short-term management of anxiety
Adult: Initially, 5 mg bid or tid, gradually increase by increments of 5 mg at 2-3 days interval. Usual dose: 15-30 mg daily in divided doses. Max: 60 mg daily.
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Short-term management of anxiety Adult: Initially, 5 mg bid or tid, gradually increase by increments of 5 mg at 2-3 days interval. Usual dose: 15-30 mg daily in divided doses. Max: 60 mg daily.
|
||||||
|
Special Patient Group
Patients taking potent CYP3A4 enzyme inhibitors: Initially, 2.5 mg once daily or bid, adjust based on clinical assessment.
|
||||||
|
Renal Impairment
|
||||||
|
Hepatic Impairment
Severe: Contraindicated.
|
||||||
|
Administration
May be taken with or without food. Take consistently either always w/ or always w/o meals.
|
||||||
|
Contraindications
Epilepsy. Concomitant use w/ MAOIs. Severe renal (CrCl <20 mL/min) or hepatic impairment. Lactation.
|
||||||
|
Special Precautions
Patient w/ acute narrow-angle glaucoma, myasthenia gravis, drug dependence. Renal or hepatic impairment.
|
||||||
|
Adverse Reactions
Nervousness, insomnia, disturbance in attention, depression, confusion, seizure, sleep disorder; dizziness, headache, light-headedness, excitement, somnolence, paraesthesia, blurred vision, coordination disorder, tremor, tinnitus; tachycardia, palpitation, chest pain; nasal congestion, pharyngolaryngeal pain; nausea, abdominal pain, dry mouth, diarrhoea, constipation, vomiting; cold sweat, rash, musculoskeletal pain, fatigue. Rarely, angioneurotic oedema, ecchymosis, urticaria.
|
||||||
|
Patient Counseling Information
This drug may cause sedation and dizziness, if affected, do not drive or operate machinery.
|
||||||
|
Monitoring Parameters
Monitor mental status.
|
||||||
|
Overdosage
Symptoms: Nausea, vomiting, dizziness, drowsiness, miosis, gastric distress, mild bradycardia, hypotension, extrapyramidal symptoms, and convulsions. Management: Symptomatic and supportive treatment w/ immediate gastric lavage. May consider activated charcoal w/in 1 hr of ingestion of >5 mg/kg.
|
||||||
|
Drug Interactions
Increased serum concentration when used w/ CYP3A4 enzyme inhibitors (e.g. erythromycin, itraconazole, nefazodone, ritonavir, diltiazem, verapamil). Decreased metabolism and therapeutic effect when used w/ CYP3A4 enzyme inducers (e.g. rifampicin). Enhanced sedative effect w/ baclofen, lofexidine, nabilone, antihistamines. May increase serum concentration of haloperidol. Buspirone does not exhibit cross-tolerance w/ sedative/hypnotics (e.g. benzodiazepine) and will not block symptoms of their withdrawal, gradually withdraw such agents prior to initiation of buspirone.
Potentially Fatal: Increased BP when taken w/ MAOIs. |
||||||
|
Food Interaction
Enhanced sedative effects w/ alcohol. Food may delay absorption and decrease first-pass metabolism, thereby increasing bioavailability. Grapefruit juice may increase buspirone concentration.
|
||||||
|
Lab Interference
May cause false-positive result on urinalysis for metanephrine/catecholamine.
|
||||||
|
Action
Description:
Mechanism of Action: Buspirone, an azaspirodecanedione, is an anxioselective drug w/ only little sedative effect but w/o anticonvulsant and muscle relaxant properties. It has high affinity for serotonin (5-HT1A and 5-HT2), moderate affinity for dopamine (D2), and no affinity for GABA receptors. Onset: W/in 2 wk. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the GI tract. Bioavailability: 1.5%-13%. Time to peak plasma concentration: W/in 40-90 min. Distribution: Volume of distribution: 5.3 L/kg. Plasma protein binding: Approx 86%-95%, mainly to albumin. Metabolism: Extensively metabolised in the liver by CYP3A4 enzyme via oxidative dealkylation to 1-pyrimidinylpiperazine as active metabolite and via hydroxylation to inactive metabolites; undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism. Excretion: Via urine (approx 29-63%, mainly as metabolites); faeces (approx 18-38%). Elimination half-life: 2-3 hr. |
||||||
|
Chemical Structure
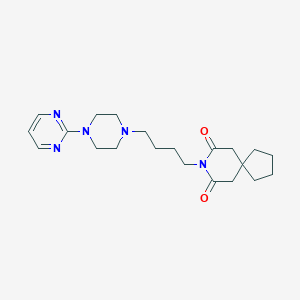 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. Buspirone, CID=2477, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Buspirone (accessed on Jan. 22, 2020) |
||||||
|
Storage
Store between 15-30°C. Protect from light.
|
||||||
|
MIMS Class
|
||||||
|
ATC Classification
N05BE01 - buspirone ; Belongs to the class of azaspirodecanedione derivatives anxiolytics. Used in the management of anxiety, agitation or tension.
|
||||||
|
References
Anon. Buspirone. Lexicomp Online. Hudson, Ohio. Wolters Kluwer Clinical Drug Information, Inc. https://online.lexi.com. Accessed 10/08/2016. Buckingham R (ed). Buspirone Hydrochloride. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 10/08/2016. Buspirone Hydrochloride Tablet (Accord Healthcare Inc). DailyMed. Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/. Accessed 10/08/2016. Joint Formulary Committee. Buspirone Hydrochloride. British National Formulary [online]. London. BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 10/08/2016. McEvoy GK, Snow EK, Miller J et al (eds). Buspirone Hydrochloride. AHFS Drug Information (AHFS DI) [online]. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 10/08/2016.
|