Miosis during surgery, Reduction of postoperative rises in intraocular pressure
Adult: As 0.01% soln: Instill up to 0.5 mL into the anterior chamber before or after securing sutures.
|
Indications and Dosage
Intraocular
Miosis during surgery, Reduction of postoperative rises in intraocular pressure Adult: As 0.01% soln: Instill up to 0.5 mL into the anterior chamber before or after securing sutures.
|
|
Contraindications
Acute iritis, anterior uveitis, some forms of secondary glaucoma.
|
|
Special Precautions
Patient w/ corneal abrasions, pre-existing retinal disease, acute cardiac failure, HTN, hypotension, recent MI, bronchial asthma, hyperthyroidism, peptic ulcer, GI spasm, urinary tract obstruction, Parkinson’s disease. Pregnancy and lactation.
|
|
Adverse Reactions
Transient symptoms of burning, stinging, and irritation of the eye; corneal clouding, persistent bullous keratopathy, post-op iritis, retinal detachment, ciliary spasm, blurred vision, lacrimation, difficulty in dark adaptation, increased pupillary block, vitreous haemorrhages, conjunctival vascular congestion, lens changes, sensitisation of the lids and conjunctiva. Rarely, nausea, vomiting, flushing, sweating, diarrhoea, headache, browache, abdominal pain, bronchial asthma and spasm, pulmonary oedema, GI distress, salivation, urinary frequency, cardiac arrhythmia, bradycardia, peripheral vasodilation leading to hypotension.
|
|
Intraocular/Ophth: C
|
|
Patient Counseling Information
This drug may cause blurred vision and difficulty in dark adaptation, if affected, do not drive or operate machinery esp at night or in poor light.
|
|
Overdosage
Symptoms: Headache, salivation, syncope, bradycardia, hypotension, abdominal cramps, vomiting, asthma, diarrhoea. Management: Supportive treatment. Treat severe systemic toxicity w/ parenteral atropine.
|
|
Drug Interactions
Decreased effectiveness w/ ophth NSAIDs and cyclopentolate. Enhanced cardiac conduction abnormalities and bronchoconstriction w/ β-blockers. Enhanced AR w/ acetylcholinesterase inhibitors.
|
|
Action
Description:
Mechanism of Action: Carbachol, a choline ester, is a quaternary ammonium parasympathomimetic that is used as a miotic. It directly stimulates muscarinic receptors of the ciliary body, facilitating trabecular drainage of aqueous humour which results in reduction of intraocular pressure (IOP). Onset: Miosis: 2-5 min (intraocular); 10-20 min (ophth). Duration: Miosis: 24 hr (intraocular); 4-8 hr (ophth). Reduction in IOP: Approx 8 hr (ophth). Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Poorly penetrates intact corneal epithelium. |
|
Chemical Structure
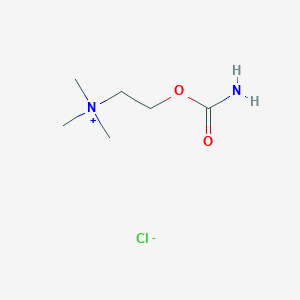 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. Carbachol, CID=5831, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Carbachol (accessed on Jan. 21, 2020) |
|
Storage
Soln for inj: Store between 15-30°C. Protect from freezing and excessive heat. Ophth soln: Store between 8-27°C.
|
|
MIMS Class
|
|
ATC Classification
S01EB02 - carbachol ; Belongs to the class of parasympathomimetics. Used in the treatment of glaucoma and miosis.
N07AB01 - carbachol ; Belongs to the class of choline esters. Used as parasympathomimetics. |
|
References
Anon. Carbachol. Lexicomp Online. Hudson, Ohio. Wolters Kluwer Clinical Drug Information, Inc. https://online.lexi.com. Accessed 10/11/2016. Buckingham R (ed). Carbachol. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 10/11/2016. McEvoy GK, Snow EK, Miller J et al (eds). Carbachol (EENT). AHFS Drug Information (AHFS DI) [online]. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 10/11/2016. Miostat Solution (Alcon Laboratories Inc.). DailyMed. Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/. Accessed 10/11/2016.
|