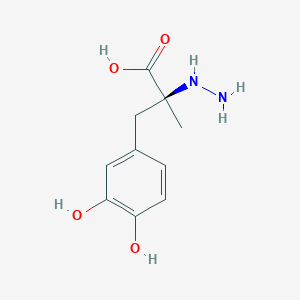
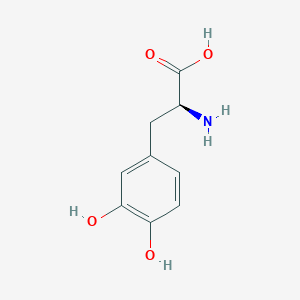
Parkinson's disease
Adult: Available preparation:
Carbidopa 4.63 mg and levodopa 20 mg per mL susp
Administer into the jejunum through a percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy with jejunal tube with an appropriate portable infusion pump. Titrate total daily dose according to therapeutic response. Max: 2,000 mg of levodopa daily.
Carbidopa 4.63 mg and levodopa 20 mg per mL susp
Administer into the jejunum through a percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy with jejunal tube with an appropriate portable infusion pump. Titrate total daily dose according to therapeutic response. Max: 2,000 mg of levodopa daily.
Oral
Parkinson's disease
Adult: Dosage is individualised based on patient’s age, cognitive status and severity of the disease and adjusted according to requirement, clinical response and tolerance.
Conventional tab:
Carbidopa 10 mg and levodopa 100 mg
Carbidopa 12.5 mg and levodopa 50 mg
Initially, 1 tab 3-4 times daily; may be increased by 1 tab every day or every other day, as required. Max: 8 tabs daily. Maintenance: At least 70-100 mg of carbidopa daily.
Carbidopa 25 mg and levodopa 100 mg
Initially, 1 tab tid; may be increased by 1 tab every day or every other day, as required. Max: 8 tabs daily. Patients on current levodopa monotherapy (<1,500 mg): 1 tab 3-4 times daily. Discontinue levodopa at least 12 hours before initiation of combination therapy. Maintenance: At least 70-100 mg of carbidopa daily.
Carbidopa 25 mg and levodopa 250 mg
Patients on current levodopa monotherapy (>1,500 mg): 1 tab 3-4 times daily. Max: 8 tabs daily. Discontinue levodopa at least 12 hours before initiation of combination therapy. Maintenance: At least 70-100 mg of carbidopa daily.
Orally-disintegrating tab (ODT):
Carbidopa 10 mg and levodopa 100 mg
1 tab 3-4 times daily; may be increased by 1 tab every day or every other day. Max: 8 tabs daily. Maintenance: At least 70-100 mg of carbidopa daily.
Carbidopa 25 mg and levodopa 100 mg
1 tab tid; may be increased by 1 tab every day or every other day. Max: 8 tabs daily. Patients on current levodopa monotherapy (<1,500 mg): 1 tab 3-4 times daily. Discontinue levodopa at least 12 hours before initiation of combination therapy. Maintenance: At least 70-100 mg of carbidopa daily.
Carbidopa 25 mg and levodopa 250 mg
Patients on current levodopa monotherapy (>1,500 mg): 1 tab 3-4 times daily. Max: 8 tabs daily. Discontinue levodopa at least 12 hours before initiation of combination therapy. Maintenance: At least 70-100 mg of carbidopa daily.
Extended-release (ER) tab:
Carbidopa 25 mg and levodopa 100 mg
Carbidopa 50 mg and levodopa 200 mg
Initially, 50 mg/200 mg bid; may be increased or decreased based on therapeutic response.
Extended-release (ER) cap:
Carbidopa 23.75 mg and levodopa 95 mg
Carbidopa 36.25 mg and levodopa 145 mg
Carbidopa 48.75 mg and levodopa 195 mg
Carbidopa 61.25 mg and levodopa 245 mg
Initially, 23.75 mg/95 mg tid for the 1st 3 days; may be increased to 36.25 mg/145 mg tid on day 4. Max: 97.5 mg/390 mg tid. Maintenance: Lowest dosage required to achieve symptomatic control. Max: 612.5 mg/2,450 mg daily.
Conventional tab:
Carbidopa 10 mg and levodopa 100 mg
Carbidopa 12.5 mg and levodopa 50 mg
Initially, 1 tab 3-4 times daily; may be increased by 1 tab every day or every other day, as required. Max: 8 tabs daily. Maintenance: At least 70-100 mg of carbidopa daily.
Carbidopa 25 mg and levodopa 100 mg
Initially, 1 tab tid; may be increased by 1 tab every day or every other day, as required. Max: 8 tabs daily. Patients on current levodopa monotherapy (<1,500 mg): 1 tab 3-4 times daily. Discontinue levodopa at least 12 hours before initiation of combination therapy. Maintenance: At least 70-100 mg of carbidopa daily.
Carbidopa 25 mg and levodopa 250 mg
Patients on current levodopa monotherapy (>1,500 mg): 1 tab 3-4 times daily. Max: 8 tabs daily. Discontinue levodopa at least 12 hours before initiation of combination therapy. Maintenance: At least 70-100 mg of carbidopa daily.
Orally-disintegrating tab (ODT):
Carbidopa 10 mg and levodopa 100 mg
1 tab 3-4 times daily; may be increased by 1 tab every day or every other day. Max: 8 tabs daily. Maintenance: At least 70-100 mg of carbidopa daily.
Carbidopa 25 mg and levodopa 100 mg
1 tab tid; may be increased by 1 tab every day or every other day. Max: 8 tabs daily. Patients on current levodopa monotherapy (<1,500 mg): 1 tab 3-4 times daily. Discontinue levodopa at least 12 hours before initiation of combination therapy. Maintenance: At least 70-100 mg of carbidopa daily.
Carbidopa 25 mg and levodopa 250 mg
Patients on current levodopa monotherapy (>1,500 mg): 1 tab 3-4 times daily. Max: 8 tabs daily. Discontinue levodopa at least 12 hours before initiation of combination therapy. Maintenance: At least 70-100 mg of carbidopa daily.
Extended-release (ER) tab:
Carbidopa 25 mg and levodopa 100 mg
Carbidopa 50 mg and levodopa 200 mg
Initially, 50 mg/200 mg bid; may be increased or decreased based on therapeutic response.
Extended-release (ER) cap:
Carbidopa 23.75 mg and levodopa 95 mg
Carbidopa 36.25 mg and levodopa 145 mg
Carbidopa 48.75 mg and levodopa 195 mg
Carbidopa 61.25 mg and levodopa 245 mg
Initially, 23.75 mg/95 mg tid for the 1st 3 days; may be increased to 36.25 mg/145 mg tid on day 4. Max: 97.5 mg/390 mg tid. Maintenance: Lowest dosage required to achieve symptomatic control. Max: 612.5 mg/2,450 mg daily.




 Sign Out
Sign Out