Dissolution of cholesterol-rich gallstones
Adult: Initially, 250 mg bid for 2 weeks, increased by 250 mg daily each week thereafter until recommend or max tolerated dose is reached. Maintenance: 13-16 mg/kg daily in two divided doses.
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Dissolution of cholesterol-rich gallstones Adult: Initially, 250 mg bid for 2 weeks, increased by 250 mg daily each week thereafter until recommend or max tolerated dose is reached. Maintenance: 13-16 mg/kg daily in two divided doses.
|
|
Hepatic Impairment
Contraindicated.
|
|
Administration
Should be taken with food.
|
|
Contraindications
Non-visualising gallbladder after two successive single doses of dye. Radiopaque stones. Gallstone complications or reasons necessitating gallbladder surgery (e.g. unremitting acute cholecystitis, cholangitis, biliary obstruction, gallstone pancreatitis, or biliary gastrointestinal fistula). Hepatic impairment, hepatocyte dysfunction or bile ductal abnormalities (e.g. intrahepatic cholestasis, primary biliary cirrhosis, sclerosing cholangitis). Pregnancy.
|
|
Special Precautions
Lactation.
|
|
Adverse Reactions
Significant: Diarrhoea, hepatotoxicity, colon cancer, gallstone recurrence.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: Leucopenia. Investigations: Increased serum transaminases, increased LDL and total serum cholesterol. Gastrointestinal disorders: Nausea, vomiting, biliary colic, abdominal cramps, abdominal pain, anorexia, constipation, dyspepsia, flatulence. |
|
Monitoring Parameters
Monitor serum aminotransferase monthly for first 3 months, then every 3 months thereafter during therapy; serum cholesterol every 6 months; oral cholecystograms and ultrasonograms at 6-9 month intervals. Confirm stone dissolution after 1-3 months of treatment.
|
|
Drug Interactions
Decreased absorption with bile acid sequestrants (e.g. cholestyramine, colestipol) and aluminium-containing antacids. Increased biliary cholesterol secretion and reduced efficacy with fibric acid derivatives (e.g. clofibrate) and oestrogen derivatives. May increase the anticoagulant effect of vitamin K antagonists (e.g. warfarin).
|
|
Action
Description:
Mechanism of Action: Chenodeoxycholic acid is a naturally occurring human bile acid. It suppresses the hepatic synthesis of both cholesterol and cholic acid, resulting in biliary cholesterol desaturation and gradual dissolution of radiolucent cholesterol gallstones. It does not exhibit any effect on radiopaque gallstones or radiolucent bile pigment stones. Synonym: chenodiol. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Distribution: Volume of distribution: Approx 1,600 L. Metabolism: Metabolised in the liver to taurine and glycine conjugates and secreted in bile; undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism and enterohepatic recycling. Further metabolised in colon by intestinal bacteria to lithocholic acid. Excretion: Via faeces (approx 80%, as lithocholate). Elimination half-life: Approx 45 hours. |
|
Chemical Structure
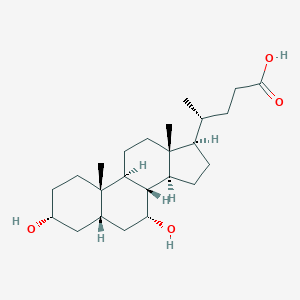 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. Chenodeoxycholic acid, CID=10133, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/10133 (accessed on June 25, 2020) |
|
Storage
Store between 20-25°C.
|
|
ATC Classification
A05AA01 - chenodeoxycholic acid ; Belongs to the class of bile acids. Used in bile therapy.
|
|
References
Anon. Chenodiol. AHFS Clinical Drug Information [online]. Bethesda, MD. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. https://www.ahfscdi.com. Accessed 10/06/2020. Anon. Chenodiol. Lexicomp Online. Hudson, Ohio. Wolters Kluwer Clinical Drug Information, Inc. https://online.lexi.com. Accessed 10/06/2020. Buckingham R (ed). Chenodeoxycholic Acid. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 10/06/2020. Chenodal Tablet, Film Coated (Manchester Pharmaceuticals Inc.). DailyMed. Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/. Accessed 10/06/2020. Chenodiol Tablet, Film Coated (Nexgen Pharma, Inc.). DailyMed. Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/. Accessed 10/06/2020. Joint Formulary Committee. Chenodeoxycholic Acid. British National Formulary [online]. London. BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 10/06/2020.
|