Iron overload in patients with thalassaemia
Adult: 25 mg/kg tid, may be adjusted according to response and therapeutic goals. Max: 100 mg/kg daily.
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Iron overload in patients with thalassaemia Adult: 25 mg/kg tid, may be adjusted according to response and therapeutic goals. Max: 100 mg/kg daily.
|
|
Administration
May be taken with or without food.
|
|
Contraindications
Neutropenia (including history of recurrent cases), history of agranulocytosis. Pregnancy and lactation.
|
|
Special Precautions
Immunocompromised patients. Hepatic and renal impairment.
|
|
Adverse Reactions
Reddish-brown urine discolouration, abdominal pain, arthralgia, neutropenia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, dyspepsia, increased ALT concentrations, headache, appetite change, asthenia, musculoskeletal pain, peripheral oedema, dizziness, somnolence, pruritus, urticaria.
Potentially Fatal: Agranulocytosis. |
|
Patient Counseling Information
This drug may cause reddish-brown discolouration of urine.
|
|
Monitoring Parameters
Monitor serum ferritin every 2-3 mth, absolute neutrophil count (ANC) at baseline and wkly during treatment (if ANC <1500/mm3, monitor CBC, WBC and platelets daily until ANC recovery); ALT mthly, Zn level, signs/symptoms of infection.
|
|
Drug Interactions
Serum concentration may be increased by UGT1A6 inhibitors (e.g. phenylbutazone). May chelate polyvalent cations, allow at least 4-hr interval w/ antacids and mineral supplements containing Al, Fe or Zn. Risk of additive toxicity w/ drugs that may cause neutropenia or agranulocytosis.
|
|
Food Interaction
Absorption may be decreased when taken w/ foods containing Fe, Al and Zn.
|
|
Action
Description:
Mechanism of Action: Deferiprone is a chelating agent w/ high affinity to ferric ion (iron III). It binds w/ ferric ions to form neutral 3:1 (deferiprone:iron) complexes. It also has low affinity to other metals including copper, Al and Zn. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Rapidly absorbed from the GI tract. Time to peak plasma concentration: Approx 1-2 hr. Distribution: Volume of distribution: 1.6 L/kg. Plasma protein binding: <10%. Metabolism: Metabolised by uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferases (UGT)1A6 to the inactive metabolite, 3-O-glucuronide. Excretion: Via urine (75-90%, as metabolite and Fe-deferiprone complex). Elimination half-life: Approx 2-3 hr. |
|
Chemical Structure
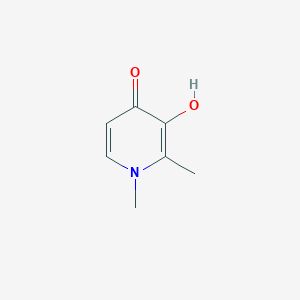 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. Deferiprone, CID=2972, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Deferiprone (accessed on Jan. 20, 2020) |
|
Storage
Store between 20-25°C. Protect from light. Any unused portions should be disposed of in accordance w/ local requirements.
|
|
MIMS Class
|
|
ATC Classification
V03AC02 - deferiprone ; Belongs to the class of iron chelating agents. Used in iron overload.
|
|
References
Anon. Deferiprone. Lexicomp Online. Hudson, Ohio. Wolters Kluwer Clinical Drug Information, Inc. https://online.lexi.com. Accessed 11/10/2016. Buckingham R (ed). Deferiprone. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com . Accessed 11/10/2016. Ferriprox Solution (ApoPharma USA, Inc). DailyMed. Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/. Accessed 11/10/2016. Ferriprox Tablet, Film-coated (ApoPharma USA, Inc). DailyMed. Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/. Accessed 11/10/2016. Joint Formulary Committee. Deferiprone. British National Formulary [online]. London. BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 11/10/2016. McEvoy GK, Snow EK, Miller J et al (eds). Deferiprone. AHFS Drug Information (AHFS DI) [online]. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 11/10/2016.
|