Atrial fibrillation, Atrial flutter
Adult: Initially, 500 mcg bid. Reduce maintenance dose if QT interval is prolonged after the 1st dose, discontinue if QT interval is >500 milliseconds.
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Atrial fibrillation, Atrial flutter Adult: Initially, 500 mcg bid. Reduce maintenance dose if QT interval is prolonged after the 1st dose, discontinue if QT interval is >500 milliseconds.
|
||||||||
|
Renal Impairment
|
||||||||
|
Administration
May be taken with or without food.
|
||||||||
|
Contraindications
Congenital or acquired long QT syndromes, baseline QT or QTc interval >440 millisecond (>500 millisecond in patients w/ ventricular conduction abnormalities). Severe renal impairment (CrCl <20 mL/min). Concurrent use of verapamil, cation transport system inhibitors and hydrochlorothiazide.
|
||||||||
|
Special Precautions
Patient w/ 2nd- or 3rd-degree heart block and/or sick sinus syndrome (unless w/ a functional pacemaker), electrolyte imbalance. Severe hepatic and renal impairment.
|
||||||||
|
Adverse Reactions
Headache, chest pain, dizziness, resp tract infection, dyspnoea, nausea, flu syndrome, insomnia, accidental injury, diarrhoea, rash, back/abdominal pain.
Potentially Fatal: Serious ventricular arrhythmias, primarily torsade de pointes. |
||||||||
|
Monitoring Parameters
Determine CrCl and QTc interval (or QT interval if heart rate is <60 beats/min) prior to initiation of therapy. Closely monitor ECG (determine QTc interval w/in 2-3 hr after the 1st dose and after each subsequent doses) for at least 3 days or 12 hr after electrical or pharmacologic conversion to normal sinus rhythm). Re-evaluate renal function and QTc interval every 3 mth thereafter. Monitor K and Mg levels at baseline and during therapy.
|
||||||||
|
Overdosage
Symptoms: Torsade de pointes. Management: Supportive and symptomatic treatment. Administer charcoal slurry w/in 15 min of dofetilide admin. Admin of isoproterenol infusion and IV Mg sulfate may be useful in managing torsade de pointes.
|
||||||||
|
Drug Interactions
Increased plasma concentration when used w/ drugs secreted by renal tubular cationic transport (e.g. amiloride, metformin, triamterene). Increased risk of toxicity when used w/ QT prolonging agents (e.g. class I/III antiarrhythmics, bepridil, cisapride, phenothiazines, TCAs, certain fluoroquinolones and oral macrolides).
Potentially Fatal: Increased risk of torsade de pointes when used w/ hydrochlorothiazide (w/ or w/o triamterene), verapamil, and renal cation transport inhibitors (e.g. cimetidine, dolutegravir, trimethoprim, ketoconazole, prochlorperazine, megestrol). |
||||||||
|
Food Interaction
Increased plasma concentration when taken w/ grapefruit juice.
|
||||||||
|
Action
Description:
Mechanism of Action: Dofetilide selectively inhibits the rapidly activating component of the K channel involved in repolarisation of cardiac cells, thereby prolonging the action potential duration and effective refractory period in both atrial and ventricular cardiac tissue. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Well absorbed. Bioavailability: >90%. Time to peak plasma concentration: 2-3 hr. Distribution: Volume of distribution: 3 L/kg. Plasma protein binding: 60-70%. Metabolism: Undergoes limited metabolism; mediated to some extent by CYP3A4 isoenzyme to form metabolites via N-dealkylation and N-oxidation. Excretion: Via urine (80%, mainly as unchanged drug and the remaining as inactive or minimally active metabolites). Terminal half-life: Approx 10 hr. |
||||||||
|
Chemical Structure
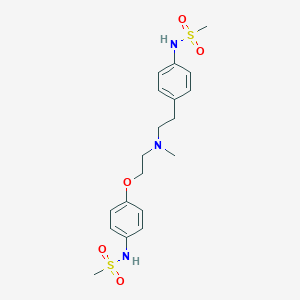 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. Dofetilide, CID=71329, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Dofetilide (accessed on Jan. 21, 2020) |
||||||||
|
Storage
Store between 20-25°C. Protect from moisture and humidity.
|
||||||||
|
MIMS Class
|
||||||||
|
ATC Classification
C01BD04 - dofetilide ; Belongs to class III antiarrhythmics.
|
||||||||
|
References
Anon. Dofetilide. Lexicomp Online. Hudson, Ohio. Wolters Kluwer Clinical Drug Information, Inc. https://online.lexi.com. Accessed 13/10/2016. Buckingham R (ed). Dofetilide. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 13/10/2016. Dofetilide Capsule (Mayne Pharma Inc.). DailyMed. Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/. Accessed 13/10/2016. McEvoy GK, Snow EK, Miller J et al (eds). Dofetilide. AHFS Drug Information (AHFS DI) [online]. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 13/10/2016.
|