Insomnia
Adult: For short-term treatment: 1-2 mg at bedtime.
Elderly: Initially, 0.5-1 mg at bedtime.
Elderly: Initially, 0.5-1 mg at bedtime.
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Insomnia Adult: For short-term treatment: 1-2 mg at bedtime.
Elderly: Initially, 0.5-1 mg at bedtime. |
|
Special Patient Group
Small or debilitated patients: Initially, 0.5-1 mg at bedtime.
|
|
Administration
May be taken with or without food.
|
|
Contraindications
Pregnancy. Concomitant use w/ ketoconazole and itraconazole.
|
|
Special Precautions
Avoid abrupt withdrawal. Hepatic and renal impairment. Elderly, small or debilitated patients. Lactation.
|
|
Adverse Reactions
Somnolence, hypokinesia, dizziness, abnormal coordination; allergic reaction, chills, fever, neck pain, upper extremity pain; flushing, palpitation; constipation, dry mouth, decreased/increased appetite, flatulence, gastritis, vomiting; thirst; arthritis, muscle spasm, myalgia; anxiety, agitation, amnesia, apathy, emotional lability, euphoria, hostility, paraesthesia, seizure, sleep disorder, stupor, twitch; asthma, cough, dyspnoea, rhinitis, sinusitis; rash, sweating, urticaria; abnormal vision, ear pain; eye irritation, pain, swelling; perverse taste, photophobia, tinnitus; frequent urination, menstrual cramps, urinary hesitancy/urgency, vag discharge/itching. Rarely, jaw pain, oedema, swollen breast; arrhythmia, syncope; enterocolitis, melaena, mouth ulceration; thyroid nodule; leucopenia, swollen lymph nodes, purpura; increased SGOT, wt gain/loss; arthralgia; ataxia, circumoral paraesthesia, decreased libido and reflexes, hallucinations, neuritis, tremor, nystagmus; epistaxis, hyperventilation, laryngitis; acne, dry skin; decreased hearing, scotomata, diplopia; haematuria, nocturia, oliguria, penile discharge, urinary incontinence.
Potentially Fatal: Anaphylaxis. |
|
Patient Counseling Information
May impair ability to drive or operate machinery.
|
|
Monitoring Parameters
Monitor resp and CV status; CBC and urinalysis periodically during prolonged use.
|
|
Overdosage
Symptoms: Somnolence, resp depression, confusion, impaired coordination, slurred speech, and ultimately, coma. Management: Supportive treatment. Gastric evacuation, either by the induction of emesis, lavage, or both, should be performed immediately. Maintain adequate ventilation. Admin IV fluids to maintain BP and encourage diuresis.
|
|
Drug Interactions
Increased plasma concentration w/ CYP3A inhibitors (e.g. nefazodone, fluvoxamine, erythromycin). Decreased plasma concentration w/ CYP3A inducers (e.g. carbamazepine, phenytoin, rifampicin, barbiturates). Additive effect w/ other CNS depressant drugs.
Potentially Fatal: Significantly increased plasma concentration w/ ketoconazole and itraconazole. |
|
Food Interaction
Alcohol may enhance the CNS effect of estazolam. Serum levels and/or toxicity may be increased by grapefruit juice.
|
|
Action
Description:
Mechanism of Action: Estazolam binds to stereospecific benzodiazepine receptors on the postsynaptic GABA neuron at several sites w/in the CNS, including the limbic system, reticular formation. Enhancement of the inhibitory effect of GABA on neuronal excitability results by increased neuronal membrane permeability to Cl ions, which results in hyperpolarisation (a less excitable state) and stabilisation. Benzodiazepine receptors and effects appear to be linked to the GABA-A receptors. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Rapidly and well absorbed from the GI tract. Time to peak plasma concentration: Approx 0.5-1.6 hr after a single 2 mg dose; 1-3 hr after a single 4 mg dose. Distribution: Widely distributed into most body tissues and fluids. Crosses the blood-brain barrier. Plasma protein-binding: 93%. Metabolism: Extensively hepatic. Excretion: Via urine (87% as inactive metabolites and <5% as unchanged drug) and faeces (4% as inactive metabolites). |
|
Chemical Structure
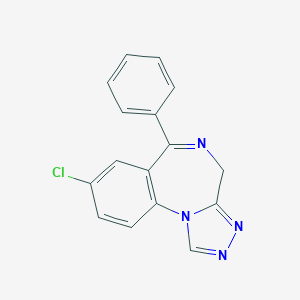 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. Estazolam, CID=3261, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Estazolam (accessed on Jan. 22, 2020) |
|
Storage
Store below 30°C.
|
|
MIMS Class
|
|
ATC Classification
N05CD04 - estazolam ; Belongs to the class of benzodiazepine derivatives. Used as hypnotics and sedatives.
|
|
References
Anon. Estazolam. Lexicomp Online. Hudson, Ohio. Wolters Kluwer Clinical Drug Information, Inc. https://online.lexi.com. Accessed 01/12/2014. Buckingham R (ed). Estazolam. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com/. Accessed 01/12/2014. Estazolam Tablet (Teva Pharmaceuticals USA Inc.). DailyMed. Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/. Accessed 01/12/2014. McEvoy GK, Snow EK, Miller J et al (eds). Estazolam. AHFS Drug Information (AHFS DI) [online]. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). https://www.medicinescomplete.com/. Accessed 01/12/2014.
|