Homozygous familial sitosterolaemia, Hyperlipidaemias
Adult: 10 mg once daily.
Child: ≥10 yr Same as adult dose.
Child: ≥10 yr Same as adult dose.
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Homozygous familial sitosterolaemia, Hyperlipidaemias Adult: 10 mg once daily.
Child: ≥10 yr Same as adult dose. |
|
Administration
May be taken with or without food.
|
|
Special Precautions
Exclude or treat secondary causes of dyslipidaemia prior to initiating therapy. Renal and hepatic impairment. Pregnancy and lactation.
|
|
Adverse Reactions
Headache, abdominal pain, diarrhoea, fatigue, chest pain, arthralgia, myalgia, anaphylaxis, erythema multiforme, angioedema, rash, and urticaria. Rarely, raised liver enzymes or hepatitis, pancreatitis, thrombocytopenia, cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, raised creatine kinase, myopathy, and rhabdomyolysis.
|
|
Monitoring Parameters
Monitor total cholesterol profile prior to therapy and periodically thereafter.
|
|
Drug Interactions
Reduced absorption w/ colestyramine. Increased plasma concentrations w/ ciclosporin. Concomitant use w/ oral anticoagulants may result in increased INR.
|
|
Action
Description:
Mechanism of Action: Ezetimibe localises at the brush border of the small intestine and inhibits absorption of cholesterol via the sterol transporter, Niemann-Pick C1-Like1 (NPC1L1). This results in decreased delivery of cholesterol to the liver, reduction of hepatic cholesterol stores and increased clearance of cholesterol from the blood. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Rapidly absorbed. Time to peak plasma concentration: 4-12 hr. Distribution: Plasma protein binding: >90%. Metabolism: Undergoes extensive conjugation in small intestine and liver to form an active glucuronide metabolite; may also undergo enterohepatic recycling. Excretion: Via bile in the faeces (approx 78% mainly as unchanged drug); urine (approx 11% mainly as metabolite). Elimination half-life: Approx 22 hr. |
|
Chemical Structure
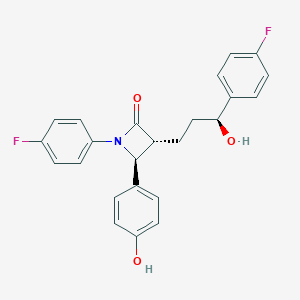 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 150311, Ezetimibe. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Ezetimibe. Accessed Apr. 26, 2022. |
|
Storage
Store at 25°C. Protect from moisture.
|
|
MIMS Class
|
|
References
Anon. Ezetimibe. Lexicomp Online. Hudson, Ohio. Wolters Kluwer Clinical Drug Information, Inc. https://online.lexi.com. Accessed 07/10/2014. Buckingham R (ed). Ezetimibe. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 07/10/2014. Joint Formulary Committee. Ezetimibe. British National Formulary [online]. London. BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 07/10/2014. McEvoy GK, Snow EK, Miller J et al (eds). Ezetimibe. AHFS Drug Information (AHFS DI) [online]. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 07/10/2014. Zetia Tablet (Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.). DailyMed. Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/. Accessed 07/10/2014. Zetia Tablets. U.S. FDA. https://www.fda.gov. Accessed 07/10/2014.
|