Overactive bladder
Adult: Initially, 4 mg once daily, increased up to max 8 mg once daily according to response. Re-evaluate patient after 8 weeks of treatment.
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Overactive bladder Adult: Initially, 4 mg once daily, increased up to max 8 mg once daily according to response. Re-evaluate patient after 8 weeks of treatment.
|
||||
|
Special Patient Group
Patient taking moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g. erythromycin, fluconazole, diltiazem, verapamil, grapefruit juice):
Renal Impairment: Mild (GFR 50-80 mL/min) to moderate (GFR 30-50 mL/min): 4 mg daily. Hepatic Impairment: Mild: 4 mg daily. |
||||
|
Renal Impairment
|
||||
|
Hepatic Impairment
Severe (Child Pugh C): Contraindicated.
|
||||
|
Administration
May be taken with or without food. Swallow whole, do not chew/divide/crush.
|
||||
|
Contraindications
Urinary retention, gastric retention, uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma, myasthenia gravis, severe ulcerative colitis, toxic megacolon. Severe hepatic impairment (Child Pugh C). Concomitant use of potent CYP3A4 inhibitors in patients with renal or hepatic impairment.
|
||||
|
Special Precautions
Patient with bladder flow obstruction (e.g. benign prostatic hyperplasia), decreased gastrointestinal motility (e.g. severe constipation), gastrointestinal obstructive disorders (e.g. pyloric stenosis), GERD, controlled or treated narrow-angle glaucoma, risk for QT prolongation (e.g. hypokalaemia, bradycardia), pre-existing cardiac diseases (e.g. MI, arrhythmia, CHF), autonomic neuropathy. Renal and mild to moderate hepatic impairment. Pregnancy and lactation.
|
||||
|
Adverse Reactions
Significant: Angioedema, CNS effects (e.g. drowsiness, dizziness, headache, blurred vision), heat prostration.
Eye disorders: Dry eye syndrome. Gastrointestinal disorders: Dry mouth, constipation. Renal and urinary disorders: UTI. Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Upper respiratory tract infection. |
||||
|
Patient Counseling Information
This drug may cause dizziness, somnolence and blurred vision, if affected, do not drive or operate machinery.
|
||||
|
Monitoring Parameters
Monitor for anticholinergic effects (e.g. dry mouth, constipation, dizziness), renal function, LFT, postvoid residual (PVR) urine volume and UTI prior to treatment initiation.
|
||||
|
Overdosage
Symptoms: Severe anticholinergic effects. Management: Symptomatic and supportive treatment. Monitor ECG. Perform gastric lavage and administer activated charcoal. Hallucinations and severe excitation may be treated with physostigmine; benzodiazepines for convulsions and pronounced excitation; betablockers for tachycardia; pilocarpine eye drops for mydriasis.
|
||||
|
Drug Interactions
Increased therapeutic and side effects (e.g. constipation, dry mouth, drowsiness, urinary retention) with other antimuscarinics and anticholinergics (e.g. amantadine, TCAs, certain neuroleptics). May reduce efficacy of metoclopramide. Increased plasma concentration with moderate (e.g. fluconazole, erythromycin) to potent (e.g. ketoconazole, clarithromycin) CYP3A4 inhibitors. Decreased plasma concentration with CYP3A4 inducers (e.g. carbamazepine, rifampicin).
|
||||
|
Food Interaction
Decreased plasma concentration with St. John’s Wort. Increased plasma concentration with grapefruit juice.
|
||||
|
Action
Description:
Mechanism of Action: Fesoterodine acts as a prodrug and is converted to its active metabolite, 5-hydroxymethyl tolterodine (5-HMT), which is responsible for its antimuscarinic activity and acts as a competitive antagonist of muscarinic receptors. It blocks the receptors in the bladder thus preventing symptoms of urgency and frequency. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Well absorbed from gastrointestinal tract. Bioavailability: 52% (5-HMT). Time to peak plasma concentration: Approx 5 hours (5-HMT). Distribution: Volume of distribution: 169 L (5-HMT). Plasma protein binding: Approx 50%, mainly to albumin and alpha1-acid glycoprotein (5-HMT). Metabolism: Rapidly and extensively hydrolysed to active metabolite, 5-HMT by non-specific esterases; further metabolised in the liver by CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 to inactive metabolites, carboxy-N-desisopropyl and N-desisopropyl. Excretion: Via urine (approx 70%; 16% as 5-HMT, approx 53% as inactive metabolites); faeces (7%). Elimination half-life: Approx 7 hours. |
||||
|
Chemical Structure
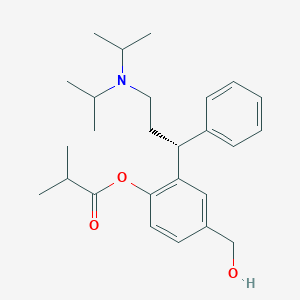 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. Fesoterodine, CID=6918558, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/6918558#section=Structures (accessed on June 26, 2020) |
||||
|
Storage
Store between 20-25°C. Protect from moisture.
|
||||
|
MIMS Class
|
||||
|
ATC Classification
G04BD11 - fesoterodine ; Belongs to the class of urinary antispasmodics.
|
||||
|
References
Anon. Fesoterodine. AHFS Clinical Drug Information [online]. Bethesda, MD. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. https://www.ahfscdi.com. Accessed 18/06/2020. Anon. Fesoterodine. Lexicomp Online. Hudson, Ohio. Wolters Kluwer Clinical Drug Information, Inc. https://online.lexi.com. Accessed 09/06/2020. Buckingham R (ed). Fesoterodine. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 09/06/2020. Fesoterodine Fumarate Tablet, Film Coated, Extended Release (Cadila Healthcare Limited). DailyMed. Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed. Accessed 09/06/2020. Joint Formulary Committee. Fesoterodine fumarate. British National Formulary [online]. London. BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 09/06/2020. Toviaz (Aesica Pharmaceuticals GmbH). MIMS Malaysia. http://www.mims.com/malaysia. Accessed 09/06/2020.
|